Uses in healthcare

Capsaicin is a compound found in chilli peppers and responsible for their burning and irritant effect. In addition to the sensation of heat, Capsaicin can also be used to relieve pain. In this article, I will draw attention to the rationale for pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmeceutical preparations. The usage of Capsaicin in obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, itch, gastric disorders, hair oil, pepper spray, etc are outlined.
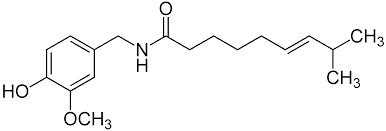
Capsaicin-Induced Analgesia
In fact, high or repeated doses of capsaicin induce an initial pain sensation that is followed by analgesia. This loss of sensitivity to painful stimuli was noticed in response to not only thermal but also mechanical and chemical noxious stimuli. Capsaicin has been used as a support pharmacological agent in pain management. Treatment with capsaicin is effective in different types of painful conditions such as complex regional pain syndromes and neuropathic pain; postsurgical neuropathic pain; post-herpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. There is also a report that repeated use of nasal capsaicin prevents cluster headache attacks. In humans, topical capsaicin (0.075%) applied four times a day for3 weeks causes the degeneration of nerve fibres of the skin and consequently decreases sensitivity to cold and tactile stimuli, but to heat and mechanical stimuli.
In patients with post-herpetic neuralgia, topical application of 8% capsaicin patch produced a significant decrease in pain for 12 weeks. A patient with post-traumatic neuropathic pain presented 80% reduction of the area of allodynia after the use of 8% capsaicin patch. This effect was observed up to the 18th month after application. Oral treatment with capsaicin candy temporarily relieves pain caused by oral mucositis, a common side effect in cancer patients in chemotherapy or radiotherapy treatment. The topical association of 3.3% tricyclic anti-depressant doxepin and 0.025% capsaicin can accelerate the development of analgesia in patients with neuropathic pain compared with the separate use of formulations.
Capsaicin concept in the pain relief is now replacing the Eucalyptus, Methyl Salicylate, Camphor & Menthol is common now. Some of the existing brands continue this old combination as part of the legal formalities as their brand was registered with these ingredients. Capsaicin is the most potential future ingredient in the counterirritant on pain relief.
Capsaicin in Weight Reduction and Obesity
Obesity is the result of an energy imbalance that develops when energy intake exceeds energy expenditure. Capsaicin can limit energy intake while it contains only negligible amounts of energy itself. Thus, great focus has been turned to studying the effect of capsaicin on energy balance. In humans, the addition of capsaicin to the diet enhances anorexigenic sensations, such as satiety and fullness. Moreover, capsaicin decreases ad libitum food intake and suppress orexigenic sensations, i.e., the desire to eat and hunger, in negative and positive energy balance.
Numerous studies have highlighted the role of thermogenesis and increase in energy expenditure (EE) in body weight regulation by capsaicin. The capsaicin alteration in gut microbial population also seems to be important in preventing high-fat diet-induced weight gain. It is noteworthy that, despite abundant evidence supporting the beneficial role of capsaicin in weight management, some studies have reported no or minimal effects of capsaicin on weight loss in humans
Capsaicin in Glucose Homeostasis and Diabetes
Capsaicin also has beneficial effects on glucose and insulin homeostasis and diabetes. Dietary and supplementation with capsaicin display an impact on glucose and insulin levels in humans. Regular consumption of capsaicin-containing chilli attenuates postprandial hyperinsulinemia in healthy adults and supplementation with it improves postprandial hyper-glycemia and hyperinsulinemia in women with gestational diabetes mellitus (DM). Further, a crossover study performed on healthy male volunteers revealed that capsaicin lowers glucose and increases insulin levels shortly after oral administration in an oral glucose tolerance test. Importantly, this study not only determined that capsaicin could be detected in the blood as early as 10 min after ingestion and levels maintained for up to 90 min, but also that capsaicin levels correlate with the lower glucose levels and maintenance of the insulin levels.
Capsaicin in Cardiovascular Conditions
The cardiovascular system is rich in capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves that play a major role in regulating cardiovascular function through the release of neurotransmitters such as CGRP, the major vasodilator, which plays an important role in regulating blood pressure under both physiological and pathophysiological conditions. Capsaicin decreases lipid storage and atherosclerotic lesions in aortic sinus and thoracic-abdominal aorta. The antioxidant property of capsaicin also contributes to their protective effects on the cardiovascular system. Moreover, it has been reported that regular consumption of chilli for 4 weeks increases the resistance of serum lipoproteins to oxidation in adult men and women. Capsaicin has been shown to inhibit platelet aggregation, which may also provide protection against cardiovascular diseases. Capsaicin anti-aggregating effect on platelets is attributed to the alteration in the fluidity of the platelet membrane.
Capsaicin in Itch
Itch elicits scratching response, whereas pain causes withdrawal responses. Treatment with a dermal patch of 0.025% of capsaicin reduces itch in psoriatic patients. In two other studies, treatment with 8% capsaicin patch reduces itch intensity and frequency in three patients with nostalgia paresthetica, and in 7 patients with neuropathic pruritus. Also, in these studies, most of the patients referred to erythema and moderate pain, pointing out to an important common side effect due to dermal capsaicin treatment.
The counter-irritant improved the blood circulation to the affected area that will help to penetrate the real active Pharma ingredient to work faster.
Capsaicin in Gastric Disorders
Daily treatment with 400 micrograms of capsaicin, three times a day, reduces ethanol- and indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal damage in healthy human subjects. The gastroprotective mechanism of capsaicin is due to the activation of the transient receptor at gastric sensory neurons which stimulates the release of neuropeptide CGRP and Nitric oxide. Capsaicin reduces H. pylori-induced gastric ulcer by reducing IL-8 production. Moreover, it is noteworthy that capsaicin per se possess bactericidal activity and inhibits H. pylori growth in vitro which may contribute to its protective effect. In fact, epidemiologic studies with 103 patients with peptic ulcer in China, and 190 in India suggest that consumption of chilli peppers is inversely proportional to the incidence of peptic ulcer pointing out to the gastroprotective effects of capsaicin.
Capsaicin Pharmaceutical Formulations
Pharmaceutical formulations for peroral administration of capsaicin are available in the form of apsules containing chilli peppers. The therapeutic dose for peroral administration of capsaicin has not been established, however, the generally recommended daily dose stated on labels of commercially available capsules is 1350–4000 mg of capsicum with 0.25% capsaicin. This range of dose has been shown to increase energy expenditure, fat oxidation, thermogenesis, and decrease appetite in humans, although both lower (0.4–2 mg) and higher (135–150 mg) doses are also effective in promoting these effects. Other pharmaceutical formulations containing capsaicin are capsicum nasal sprays and homeopathic preparation of Capsicum annum and Eucalyptol nasal sprays. These formulations have been used to treat non-allergic rhinitis and the symptoms associated with this condition. Although a therapeutic dose has not been established yet, a previous study has shown that 4 microgram/puff of capsicum, three times a day for three consecutive days, is efficacious for non-allergic, non-infectious perennial rhinitis.
Capsaicin in hair oils & Shaving Cream.
The topical use of capsaicin along with hair oil can increase blood flow, which is key to having a healthy scalp and hair. A 2007 study found that “Capsaicin promotes hair growth in mice and humans with alopecia,” In cold climate area making the hair oil waring feels and the active ingredients in the hair oil penetrate much faster and give a better result.
Men like the light hot feeling in Shaving cream as most of the anti-septic after shave lotion in the market has this unique sale-oriented technique.
Capsaicin in other industry
Presently companies are exploring the potential of Capsaicin as an additive in paint manufacturing; especially Algae prone area to claim weather guard protection
• As an Anti-Microbial additive in Decorative paint formulation to prevent micro-organisms growth during storage/ after application.
• As an additive in demineralized water used in waterborne paints to avoid algae, fungus growth
• Maybe used as an organic biocide in Antifouling paints to replace highly toxic/regulated chemical biocides.
• Maybe used in potable water pipeline coatings to inhibit the growth of microorganisms inside and outside the pipeline
• Maybe used as an additive in Packaging Coating to impart antimicrobial properties to food/beverage storing containers.
• Maybe of use in the medical field as an antimicrobial ingredient in coatings applied over medical equipment.
• Maybe of use in the anti-termite, antifungal, antibacterial properties of Capsaicin in Golf courses and home lawns?
• Maybe of use in the buildings are built in wood should require such an all-natural ATT.
• Maybe of use in Water storage area as Capsaicin coting to avoid fungal growth (European Toilet seat is most potential are in cold countries under the toilet seat coating with Capsaicin).
Organic farming to avoid pests, Police/Military to control violence group by adding 50gms in 12000Lts water Tanker, Ladies bodyguard sprays, The Cable industry, and Storage Go down Electrical waring area to keep the Capsicum Sachets in Cable Joints …The application is unlimited.
As we can see, Capsaicin has got a potential role to play in the packing industry with GO GREEN being the need of the hour. But what restricts its entry into the field is the lack of lab-generated data to substantiate its functional roles in water PVC pipe to avoid fungus.
Capsaicin and food-containing capsaicin have been together with humans over thousands of years, but only more recently that our understanding of how capsaicin affects our organism has significantly advanced. Capsaicin importance is corroborated by the varied pharmaceutical/
nutraceutical/cosmeceutical formulations. Despite being an old molecule, capsaicin is still a hot topic in the scientific community and presents a wide horizon of potential therapeutic uses. Therefore, new pharmaceutical formulations, development of new analogy, or targeting the capsaicin-activated receptor TRPV1 are promising pharmacological approaches in the following years.




